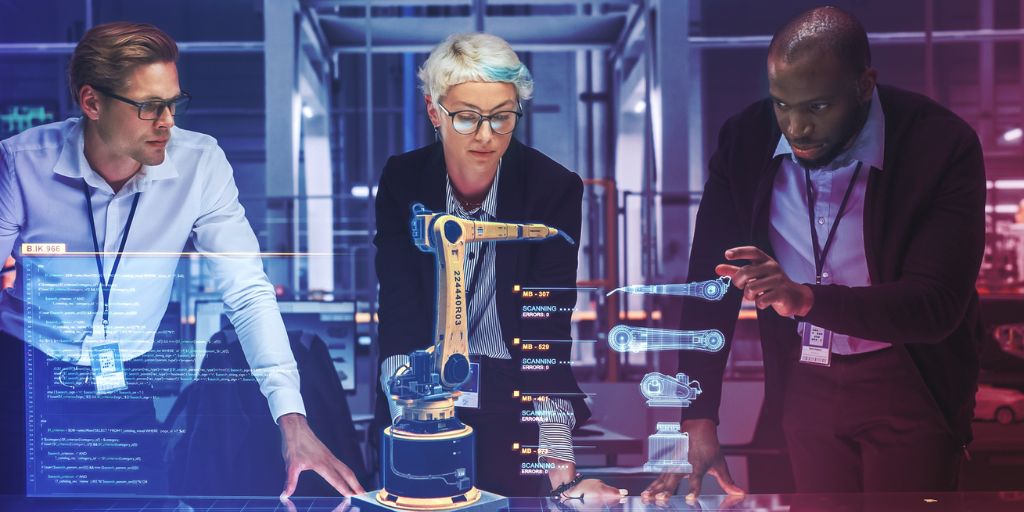
The healthcare industry is experiencing a digital revolution, with software integration becoming an integral part of the patient experience. In the post-pandemic era, healthcare organizations are increasing their software investments, even in the face of economic uncertainty. According to the Future of Healthcare Report, a staggering 80% of US health systems plan to invest in digital health technologies by 2025.
In the last six months, the healthcare IT industry has witnessed many significant digitalization waves, from new regulations over interoperability, predictive analytics, and medical AI, to AI testing of those very applications. These milestones of progress are unlocking exciting opportunities for the industry.In the meantime, an increasingly complex, connected software ecosystem is also driving the need for AI-driven software test automation tools that can help accelerate digital health innovations while ensuring care quality.
So, what does the rest of 2023 have in store for healthcare IT? Read on for five key considerations on what to expect in the second half of 2023.Trend 1: The Demand for Telehealth Continues to GrowTelehealth, a mere sideline player before the pandemic, is becoming more mature, or what some call Telehealth 2.0.In a recent American Medical Association (AMA) survey, over 8 out of 10 physicians reported the current use of telehealth. Despite the uncertain economic environment, the US telehealth market will reach $309 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45.1% due to the following factors.• Increasingly growing patient acceptance: 58% of US consumers are interested in telehealth replacing in-person visits because of convenience and speed of care.• Reduced cost of a healthcare plan: 55% of providers expect telehealth to lower healthcare costs over the next three to five years.• Shifting from urgent to specialized care: key telehealth providers are expanding specialized virtual clinics to treat high-cost chronic conditions such as kidney disease, diabetes, and migraines.Telehealth also gives rise to a new class of connected devices and mobile applications that integrates seamlessly with other hospital systems. Interoperability is essential to streamline data sharing to improve care coordination. With the rise of telehealth, more healthcare organizations are opting for automated cross-platform testing to comply with HIPAA, the Cures Act, and other regulations.
Trend 2: AI Drives Tremendous Opportunities to Improve Healthcare ServicesVarious AI and machine learning (ML) technologies, including generative AI, have made to headlines and touched many aspects of our lives, with more providers realizing the benefits of AI in healthcare.The power of AI lies in its ability to derive actionable insights quickly from massive amounts of data to enable healthcare organizations to boost productivity and reduce costs. According to Accenture, by 2026, AI could save the healthcare industry over $150 billion per year, including robot-assisted surgery ($40 billion), virtual nursing assistants ($20 billion), and administrative workflow assistance ($18 billion). Specifically, computer vision algorithms help physicians analyze medical imagery in just seconds to detect early warning signs of diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. Pharma companies are also evaluating AI models to accelerate drug discovery and development. Providers can use AI to identify more effective care paths based on millions of medical studies to offer hyper-personalized treatment.Outside of frontline clinical work, AI also has wider applications in healthcare software testing — the ability to auto-generate test cases and expand the test coverage beyond linear paths. This process enables the software testing teams to uncover more unexpected user journeys and deliver better software faster.
Trend 3: Two Key Challenges Push the Automation EnvelopeTwo industry challenges – workforce shortages and financial pressures – are driving healthcare organizations to embrace automation.The pandemic has intensified medical workforce shortages, leading to increased patient loads and physician burnout. According to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMCs’) prediction, the US is facing a dangerous shortage of up to 124,000 physicians within 11 years. Automation technologies like robotics process automation (RPA) can enhance productivity and alleviate burnout.Financial pressures have been another primary incentive behind investments in automation. Given the current fluctuating nature of most health systems’ balance sheets, higher operational efficiency means greater resilience. To navigate these challenges, more healthcare organizations will pivot to robotics process automation (RPA). Providers can benefit from RPA in multiple ways, from reduced administrative tasks to quality control improvements and higher operational efficiency.As the technology becomes increasingly mature, forward-thinking tech leaders are now leveraging the combination of RPA and AI to maximize automation benefits at scale – welcome to the age of RPA 2.0. With the walk-in by AI, RPA 2.0 brings many more benefits beyond efficiency gains. It unlocks new abilities such as natural language processing (NLP), character and image recognition, and enabling bots to see, think, and even improvise. Ultimately, you can expect them to be self-guiding to:• Automate more complex cognitive or decision-making processes.• Process a broader range of documents (handwriting, email, scan, and image) by analyzing both structured and unstructured data.• Understand information on the screen with intelligent computer vision.
Trend 4: Healthcare Organizations Invest More in AIoT DevicesThe Internet of Things (IoT) continues to transform healthcare, and the advent of the Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) presents even greater opportunities. AIoT enables a connected network of medical devices, improving patient outcomes and reducing the strain on healthcare systems. Three main AIoT opportunities are:Remote patient monitoring (RPM)According to Forrester, about one out of four US patients with chronic diseases will receive treatment by RPM by 2023.WearablesThe global wearable healthcare device market is projected to go over $150 billion in two years, a big incentive for tech giants, health insurers, and health systems to consider joining the wearables market. New wearable devices will become available in the consumer market to empower patients to collect and analyze their health data and make better decisions about taking care of themselves. In-clinic IoTTraditional healthcare institutions are also adding IoT connectivity to their hospitals. For example, they can use sensors for informed decision-making based on real-time monitoring of patients and equipment. This trend continues to gain momentum as IoT plays a more significant role in driving hospital efficiency.Healthcare IT leaders must be aware of IoT’s data privacy and security concerns. Software testing strategies must keep up with the increasing complexity and connectivity to ensure all IoT devices function as expected and to keep patient data secure.
Prediction 5: Establishing Security in the Entire Software StackHealthcare faces increasing cybersecurity threats, making security a top priority. Connected medical devices pose vulnerabilities, and the cost of data breaches in healthcare is soaring. According to IBM, the cost of data breaches in healthcare is fast approaching $10 million. As software becomes more prevalent in healthcare, so will the need for advanced trust and security at all system levels. From a testing perspective, automation technologies are essential to keep software up to date, secure, and compliant with regulations like HIPAA.In summary, the digital transformation of healthcare is accelerating, and the industry must embrace smarter, faster, and more secure testing tools.Keysight Eggplant is dedicated to enabling digital innovation in healthcare by providing AI-driven healthcare software testing solutions. With well-defined testing strategies, healthcare organizations can ensure a consistent patient experience across multiple systems, safeguarding the future of healthcare in the years to come.